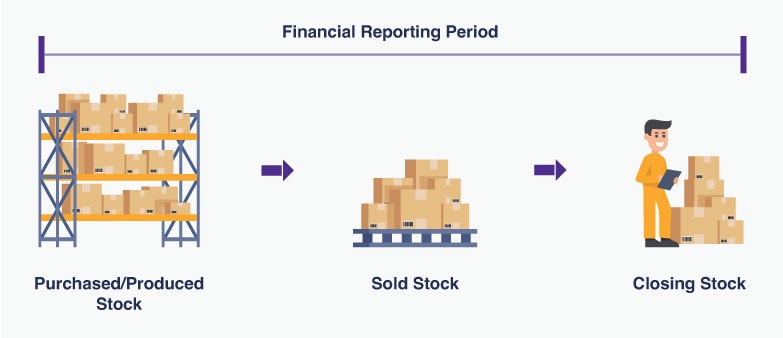
About Inventory Valuation
Inventory is the lifeline of any manufacturing enterprise, be it parts, sub-assemblies, raw materials, semi-finished, finished products, and even repair, maintenance, and operating goods. Every inventory item holds a certain value and manufacturers have to calculate this value accurately at the end of the financial year. This is called Inventory Valuation.
Let’s take an example,
A manufacturer who is into the production of fashion clothing such as t-shirts, trousers, shirts, etc. has inventory in the form of fabric materials, buttons, zippers, threads, dyes, printing designs, etc. It also includes packaging materials, tag cards, and cartons.
All of these if unsold or unused are called inventory stock and considered a current asset for the organization. This means they hold a certain financial value till they are consumed to manufacture finished products and sold in the market.
Apart from materials, there are other factors as well that come under inventory valuation.
Direct Materials
As mentioned above, the cost of direct raw materials and semi-finished goods that go into the final product. This cost can be arrived at using actual cost or standard cost.
Direct Labor
To calculate inventory valuation, only the labor responsible to manufacture the product is taken into account. Factors such as wages, pension contributions, payroll taxes, insurance, etc. are taken into account while calculating inventory valuation.
Overhead Costs
Cost of utilities, rent, insurance, equipment, tools, maintenance, and repair incurred during goods production.
Transport & Logistics
Transportation and logistics costs that are incurred during transporting the goods within the facility and customer delivery.
Material handling
Costs incurred to ready the finished goods for customer shipment (goods picking, packing, shipping label generation, and final shipment).
Taxes
Any taxes paid to import raw materials.
Sunken Costs
Costs incurred due to an error in the manufacturing process.
Now, if the manufacturer has 500 t-shirts, 500 shirts, and 500 pairs of trousers left unsold at the end of the financial year, the value for each item needs to be calculated and accounted for in the company’s balance sheet.
The Role of Costing Methods in Inventory Valuation
There are several methods employed by manufacturers to arrive at the cost of an item. These are,
Actual Costs
Actual costs as the name suggests, are derived based on the actual cost incurred for materials, labor, and overheads. Actual costs are derived from landed costs.
Actual Cost = Direct Costs + Indirect Costs + Fixed Costs + Variable Costs + Sunken Costs
What is Landed Cost?
Landed cost is the total price of a product that a buyer has to pay after he/she receives it at the doorstep. Landed costs include manufacturing costs, shipment fees, taxes, insurance, packaging fees, material handling, etc.
Actual costs are usually compared with estimated or planned costs to arrive at a variance.
Standard Costs
Standard costs are pre-determined costs based on specific working conditions and taking into account, a standard time and cost measurement of machines, labor, and materials.
Standard costs are usually compared with the Actual Costs for maximum accuracy.
Importance of Inventory Valuation in Manufacturing
The manufacturer would have paid a certain value to procure, store, transport, and maintain raw materials. Also, these items would have been procured at different costs at different timelines of the year. Therefore, a certain valuation method needs to be adopted in order to arrive at a common cost.
Inventory valuation has a direct impact on the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), gross income, margins, and profitability and therefore manufacturers should accurately calculate valuation costs. This also has an impact on tax filing and regulatory compliance.
Inventory Valuation Methods
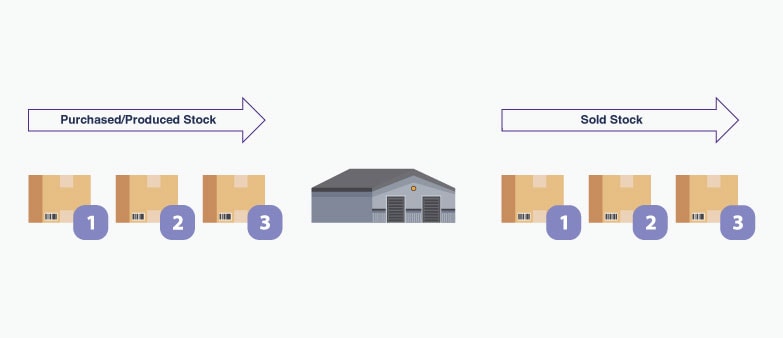
FIFO (First In, First Out)
Most manufacturers use the FIFO method to evaluate their inventory. FIFO as the name suggests means that the first batch of products that they manufacture and sell is from the first batch of raw materials that they bought. They take into account the costs pertaining to the first batch of raw materials while calculating the inventory.
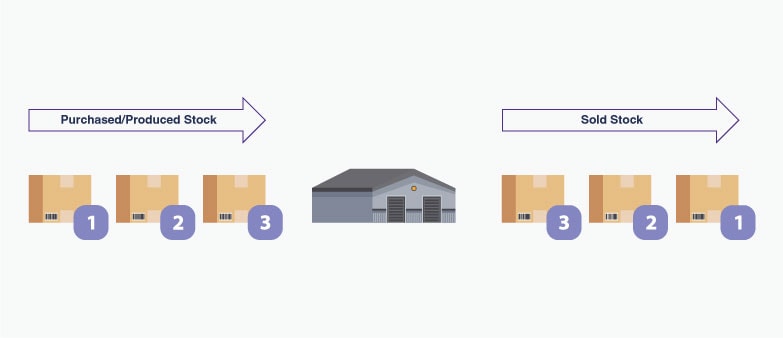
LIFO (Last In, First Out)
LIFO as the name suggests means that the first batch of products that they sell is from the last batch of raw materials.
WAC (Weighted Average Cost)
In the WAC method, the average cost is calculated by dividing an item’s inventory cost throughout the year by the number of items.
Specific Identification
In this method, every inventory item is tracked from the time its purchased, and stocked till its sold. This method is used in the case of larger items that are easily differentiated from each other.
Out of the four, FIFO is the most widely used method as it reduces the COGS and higher gross income. However, the taxes increase due to high gross income. In LIFO, the COGS increases whereas the taxes decrease.
How does ERP software help manufacturers in accurately calculating Inventory Valuation?
With ERP software’s integrated modules, manufacturers can choose a suitable inventory valuation method and instantly arrive at accurate inventory valuation methods.
All incoming raw materials, parts, and assemblies are tagged with bar codes or RFID tags and product information is instantly recorded in the ERP. The information also includes each item’s value, quantity, and date of purchase. Finished products are also tagged with bar-codes/RFID tags and recorded into the ERP system.
All this data goes into the ERP’s centralized database which becomes useful when calculating the value at the end of the financial year.
Manufacturers have an option to choose a valuation suitable method (most commonly FIFO) at the start of the financial year within the ERP. This ensures that they have a consistent valuation throughout the year.
They also have an option to choose and assign a suitable valuation method to a particular item category. A category can contain items having identical attributes grouped together to avoid complexity. Different categories can be assigned different valuation methods based on the item property and usage type.
Modern ERP software provides manufacturers to include costing methods to calculate inventory valuation. For example, they can select the landed cost method which basically enables the ERP to add various costs at each manufacturing stage of an item, such as production, packaging, shipping, handling, taxes, duties, insurance, etc, and arrive at a single landed cost.
Some ERP software provides an option to add a service/goods cost to the original product cost without a PO. For example, if a manufacturer has bought materials from a certain vendor but the vendor won’t transport them to the warehouse. The manufacturer has to appoint a third-party shipment contractor to transport the goods. Most of the time, these are one-off activities and a PO isn’t raised, but manufacturers can add the transport cost to the original product cost.
Conclusion
Inventory is a crucial asset for manufacturers and accurately determining its value is equally important. A thorough understanding of inventory valuation and scientific methods of arriving at an accurate value has a profound impact on bookkeeping. Also, knowing the true asset values paves way for long-term growth and expansion plans.
OmegaCube ERP’s integrated accounting and inventory modules help manufacturers efficiently evaluate their inventory assets.
Contact us for an in-depth demo.