Manufacturers face a whole lot of challenges when it comes to managing their business. Most of these challenges can be solved with technological advancements that are in place today. After all, manufacturing industry is no stranger to technological innovations since the advent of steam engines and assembly lines.
In today’s world, manufacturers are facing the biggest challenge of them all. Data.
How?
Manufacturers often tend to get overwhelmed when they realize how much data their production floor generates in a single day. Imagine, months and years. Most of this data goes unused as research suggests that only 1% is used to detect anomalies in production processes, machine deficiencies and breakdowns etc. and rectify them.
With data being collected and managed in legacy enterprise software and isolated systems in different departments, it becomes difficult for manufacturers to take benefit of their entire data set and derive useful insights out of it.
Manufacturers are vastly unaware of Big Data technology solutions that can put their vast data trove to good use and benefit their organization. Instead of focusing only on past activities and being reactive to disruptions, these systems can actually help them to be proactive and predict the future. Sounds like a science fiction movie? Not any longer. It is the reality now and Big Data is at the helm of it.
With the right technology and knowing what goals to achieve, where to look and how to make optimum use of data, manufacturers can reap instant dividends through Big Data Analytics.
Let’s understand Big Data in further detail.
- What is Big Data?
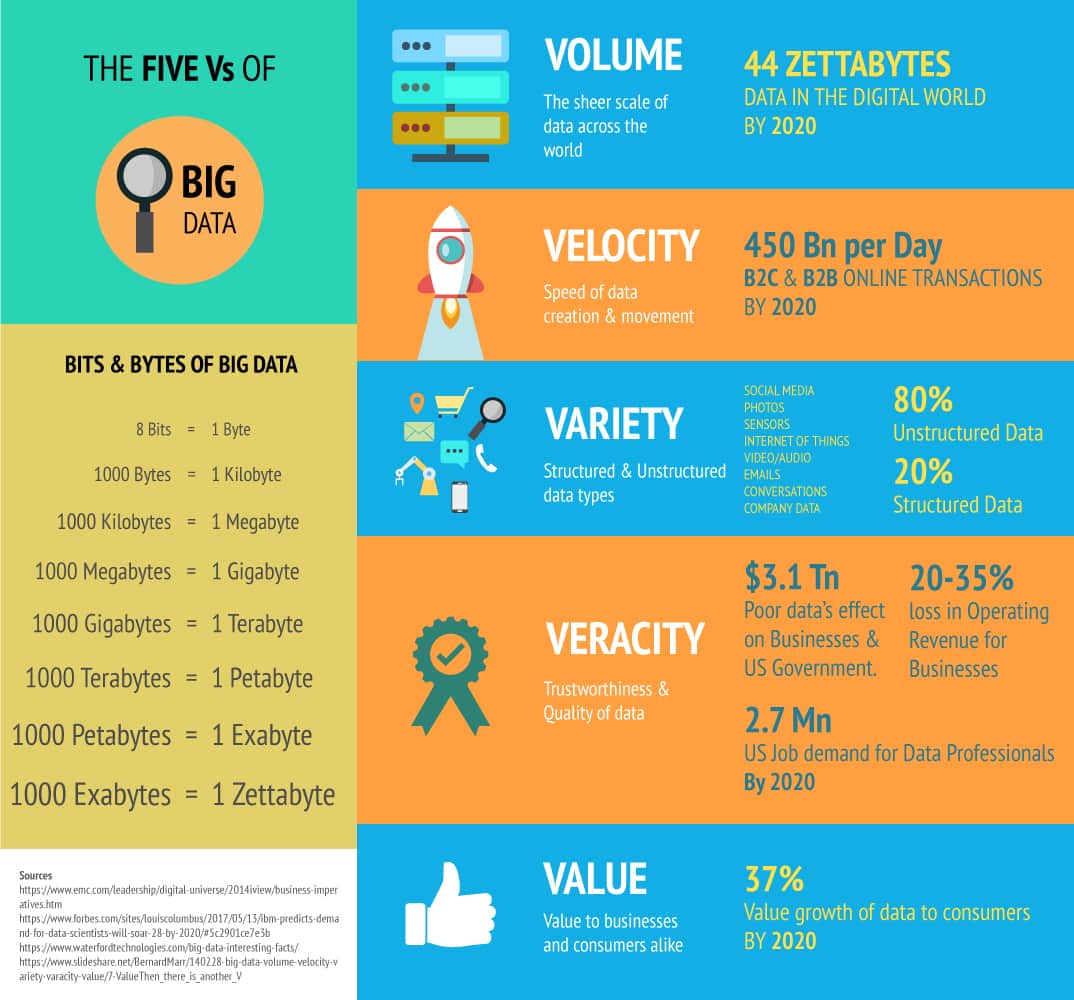
- The Five Vs of Big Data
- Sources of Data
- ERP & MES Systems
- Machine Monitoring Devices
- Marketing Activities
- Research & Development
- Overwhelming or Intriguing?
What is Big Data?
The entire world is constantly talking about Big Data. But what is it exactly?
Big Data consists of large, complex data-sets captured in a centralized database location from different sources that are a part of a unified technological environment within an organizational entity.
These data-sets cannot be handled by traditional data processing software, and need a completely different set of technology to capture, store, search, analyze, visualize, and update data with robust security and privacy controls.
The Five Vs of Big Data
Sources of Data
ERP & MES Systems
Being a manufacturer, chances are high that you are using a latest ERP & MES system. These systems collects minute-by-minute happenings on production process, personnel & machine performance, supply chain efficiency, production controls, inventory movement, sales transactions, order transactions etc. from various departments and shop floor. This data is stored in a common database. Data points are often inter-connected to each other and provides total visibility and historical data to the manufacturer. Tapping into this resource alone can yield varied data points and insights that the manufacturer can utilize to fine tune their business processes and workflows.
Machine Monitoring Devices
The rise of Internet of Things (IOT) has made sensors and sensor-based technology, very cost effective and affordable. Manufacturers can now install these sensors on their machines thereby tracking minute-by-minute information such machine downtime/uptime/idle time, operating personnel details, total job time, scrap generated, yield quality etc. Apart from it, these sensors also monitor machine temperature, sound, vibrations, flow-rate, weight, humidity, air pressure etc. In case of any abnormal observances, the sensors throw an alert thereby initiating replacement/repair even before a potential breakdown. This prevents machine breakdown and subsequent delay in production along with associated costs and inconvenience to customers/suppliers.
Marketing Activities
Lot of data is collected during the course of marketing activities such as, lead generation activities on the website, form fills, email campaigns, advertising campaigns, trade-shows, product events, customer surveys, cold-calling, social media campaigns, feedback mechanisms etc.
This data sits on various platforms such as website, industry forums, social media, mass-mail platforms, CRM system, excel spreadsheets and usually require a person to track, collate this data into a single tool. The data is generally useful to understand buying preferences & patterns of customers, customer feedback and grievances, product requirements, product defects, pricing preferences, etc. and use them to iron out respective processes, improve product quality and functionality.
Research & Development
The R&D department constantly work on enhancing the product, innovate using latest technologies or design a new product altogether. During the product design and development lifecycle, lot of data is created, collected and tracked. This data can be analyzed to find out process improvements in design and development of the product, decrease the overall time-to-market period, and design a better product that is strictly based on concrete data. This data-driven product development ensures, their products are accurately based on what the customer needs thereby driving customer satisfaction, reduced after-sales spending and fewer product issues.
Overwhelming or Intriguing?
Definitely intriguing if you are looking for long-term business growth.
You have got a full picture of the data you possess within your organization. This data increases based on the scale and setup of your manufacturing business. Bigger the setup, more the data.
The data is more like a ball of clay in your hands. It becomes useful only when you mold it as per your requirement and convert it into a more useful entity. By this, we mean analyzing it with the help of various analytical tools, derive inputs in the form of emerging patterns, trends, behavior, and accordingly modify and improve your workflows, controls and processes.
So how do you go about it? Stay tuned for our next blog on Big Data.




Fantastic site you have here but I was curious if you knew of any discussion boards that
cover the same topics discussed here? I’d really love to be a part of group where I can get opinions from other experienced individuals that share the same
interest. If you have any suggestions, please let
me know. Bless you!